Bryson-Denham Problem (Short version)
Contents
Problem description
The Bryson-Denham Problem but we take advantage of the propt input format to compute the cost function directly, without going via u and x3.
% Copyright (c) 2007-2008 by Tomlab Optimization Inc.
Problem setup
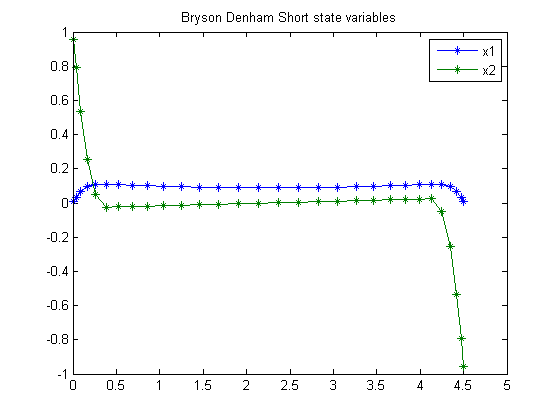
toms t tf p = tomPhase('p', t, 0, tf, 30); setPhase(p); tomStates x1 x2 x1max = 1/9; x0 = {tf == 0.5}; constr = {0.001 <= tf <= 50 collocate({0 <= x1 <= x1max; -10 <= x2 <= 10}) initial({x1 == 0; x2 == 1}); final({x1 == 0; x2 == -1}) collocate(dot(x1) == x2)}; options = struct; options.name = 'Bryson Denham Short'; solution = ezsolve(integrate(0.5*dot(x2).^2), constr, x0, options); t = subs(collocate(t),solution); x1 = subs(collocate(x1),solution); x2 = subs(collocate(x2),solution); figure(1) plot(t,x1,'*-',t,x2,'*-'); legend('x1','x2'); title('Bryson Denham Short state variables');
Problem type appears to be: con
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Bryson Denham Short f_k 3.975295744665011900
sum(|constr|) 0.000000002213305771
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 3.975295746878317900
f(x_0) 1859.999999999970900000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 139 GradEv 137 ConstrEv 137 ConJacEv 137 Iter 136 MinorIter 413
CPU time: 0.328125 sec. Elapsed time: 0.328000 sec.