Bryson-Denham Two Phase Problem
An example of how the input could look for PROPT.
Contents
Problem description
In this example we also take advantage of the advance knowledge that the solution reaches x1=x1max with x2=0, to introduce an event that divides the time interval into two phases. This increases the accuracy of the solution.
% Copyright (c) 2007-2008 by Tomlab Optimization Inc.
Problem setup
for n=[5 21]
toms t1 tcut p1 = tomPhase('p1', t1, 0, tcut, n); toms t2 tmax p2 = tomPhase('p2', t2, tcut, tmax-tcut, n); setPhase(p1); tomStates x1p1 x2p1 tomControls up1 setPhase(p2); tomStates x1p2 x2p2 tomControls up2 % Constant x1max = 1/9; setPhase(p1); % Initial guess if n==5 x01 = {tcut == 0.25 tmax == 0.5 icollocate({ x1p1 == 0 x2p1 == 1-2*t1/tcut }) collocate(up1==0)}; else x01 = {tcut == tcut_opt tmax == tmax_opt icollocate({ x1p1 == x1p1_opt x2p1 == x2p1_opt }) collocate(up1==up1_opt)}; end % Box constraints cbox1 = {0.001 <= tcut <= tmax-0.01 tmax <= 50 collocate({0 <= x1p1 <= x1max -10 <= x2p1 <= 10})}; % Set up initial conditions in phase p1 % Initial constraints cbnd1 = initial({x1p1 == 0; x2p1 == 1}); % ODEs and path constraints ceq1 = collocate({ dot(x1p1) == x2p1 dot(x2p1) == up1}); % We take advantage of the fact that we've determined that a good place to % shift between phases is when x1 reaches x1max, and that x2 must equal 0 % there (Later, we want the solver to be able to figure this out for % itself). % Final constraints cbnd1 = {cbnd1 final({x1p1 == x1max; x2p1 == 0})}; % Using integral gives the integral over the phase of an expression - % in this case 0.5 times the square of u. % Objective objective1 = integrate(0.5*up1.^2); setPhase(p2); % Initial guess if n==5 x02 = {icollocate({ x1p2 == 0 x2p2 == 1-2*t2/tmax }) collocate(up2==0)}; else x02 = {icollocate({ x1p2 == x1p2_opt x2p2 == x2p2_opt }) collocate(up2==up2_opt)}; end % Box constraints cbox2 = collocate({0 <= x1p2 <= x1max -10 <= x2p2 <= 10}); % ODEs and path constraints ceq2 = collocate({ dot(x1p2) == x2p2 dot(x2p2) == up2}); % x2_i of p2 is already linked to x2_f of p1, but linking it to a constant % helps convergence. % Final conditions in phase p2. cbnd2 = {initial(x2p2 == 0) final(x1p2 == 0) final(x2p2 == -1)}; objective2 = integrate(0.5*up2.^2); % Link the phases link = {final(p1,x1p1) == initial(p2,x1p2) final(p1,x2p1) == initial(p2,x2p2)};
Solve the problem
options = struct;
options.name = 'Bryson Denham Two Phase';
objective = objective1+objective2;
constr = {cbox1, cbnd1, ceq1, cbox2, cbnd2, ceq2, link};
solution = ezsolve(objective, constr, {x01, x02}, options);
x1p1_opt = subs(x1p1, solution);
x2p1_opt = subs(x2p1, solution);
up1_opt = subs(up1, solution);
x1p2_opt = subs(x1p2, solution);
x2p2_opt = subs(x2p2, solution);
up2_opt = subs(up2, solution);
tcut_opt = subs(tcut, solution);
tmax_opt = subs(tmax, solution);
Problem type appears to be: con
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Bryson Denham Two Phase f_k 3.999999993412736800
sum(|constr|) 0.000000023177918609
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 4.000000016590655100
f(x_0) 0.000000000000000000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 39 GradEv 37 ConstrEv 37 ConJacEv 37 Iter 34 MinorIter 69
CPU time: 0.062500 sec. Elapsed time: 0.078000 sec.
Problem type appears to be: con
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Bryson Denham Two Phase f_k 3.999999995253987500
sum(|constr|) 0.000000000347325270
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 3.999999995601312800
f(x_0) 3.999999738804261200
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 4 GradEv 2 ConstrEv 2 ConJacEv 2 Iter 1 MinorIter 75
CPU time: 0.046875 sec. Elapsed time: 0.046000 sec.
end
t = subs(collocate(p1,t1),solution);
t = [t;subs(collocate(p2,t2),solution)];
x1 = subs(collocate(p1,x1p1),solution);
x1 = [x1;subs(collocate(p2,x1p2),solution)];
x2 = subs(collocate(p1,x2p1),solution);
x2 = [x2;subs(collocate(p2,x2p2),solution)];
Plot the result
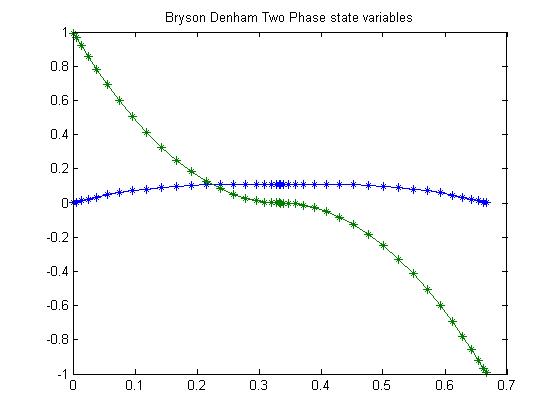
figure(1) plot(t,x1,'*-',t,x2,'*-'); title('Bryson Denham Two Phase state variables');