Fuller Phenomenon
A Short Introduction to Optimal Control, Ugo Boscain, SISSA, Italy
3.6 Fuller Phenomenon.
Contents
Problem Description
Find u over t in [0; inf ] to minimize:
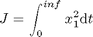
subject to:
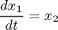
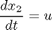
![$$ x(t_0) = [10 \ 0 ] $$](xfullerPhenomenon_eq30483.png)
![$$ x(t_f) = [0 \ 0 ] $$](xfullerPhenomenon_eq53886.png)
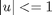
% Copyright (c) 2007-2008 by Tomlab Optimization Inc.
Problem setup
toms t toms tf p = tomPhase('p', t, 0, tf, 60); setPhase(p); tomStates x1 x2 tomControls u % Initial guess x0 = {tf == 10 icollocate(x1 == 10-10*t/tf) icollocate(x2 == 0) collocate(u == -1+2*t/tf)}; % Box constraints cbox = {1 <= tf <= 1e4 -1 <= collocate(u) <= 1}; % Boundary constraints cbnd = {initial({x1 == 10; x2 == 0}) final({x1 == 0; x2 == 0})}; % ODEs and path constraints ceq = collocate({dot(x1) == x2; dot(x2) == u}); % Objective objective = integrate(x1.^2);
Solve the problem
options = struct; options.name = 'Fuller Phenomenon'; options.solver = 'snopt'; solution = ezsolve(objective, {cbox, cbnd, ceq}, x0, options); t = subs(collocate(t),solution); x1 = subs(collocate(x1),solution); x2 = subs(collocate(x2),solution); u = subs(collocate(u),solution);
Problem type appears to be: con
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Fuller Phenomenon f_k 242.423532418144450000
sum(|constr|) 0.000000063717015571
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 242.423532481861460000
f(x_0) 333.333333333328820000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 28 GradEv 26 ConstrEv 27 ConJacEv 26 Iter 14 MinorIter 236
CPU time: 0.187500 sec. Elapsed time: 0.187000 sec.
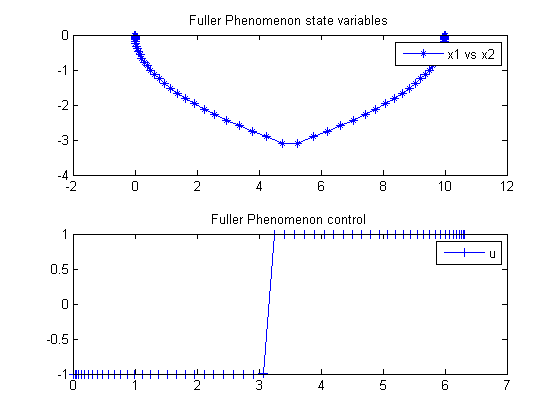
Plot result
subplot(2,1,1) plot(x1,x2,'*-'); legend('x1 vs x2'); title('Fuller Phenomenon state variables'); subplot(2,1,2) plot(t,u,'+-'); legend('u'); title('Fuller Phenomenon control');