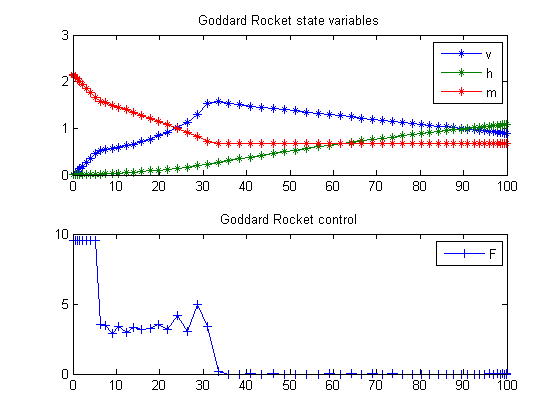
Goddard Rocket, Maximum Ascent, Final time fixed, Singular solution
Example 7.2 (ii) from the paper: H. Maurer, "Numerical solution of singular control problems using multiple shooting techniques", Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, Vol. 18, No. 2, 1976, pp. 235-257
Remark: You can vary the fixed final time tf to obtain Fig. 8 in the paper
L.G. van Willigenburg, W.L. de Koning
Copyright (c) 2007-2009 by Tomlab Optimization Inc.
Contents
Problem setup
toms t % Parameters alpha = 0.01227; beta = 0.145e-3; c = 2060; g0 = 9.81; r0 = 6.371e6; r02=r0*r0; m0 = 214.839; mf = 67.9833; Fm = 9.525515; tf = 100; %Paper value 206.661;
Solve the problem, using a successively larger number of collocation points
for n=[20 40 60] p = tomPhase('p', t, 0, tf, n); setPhase(p); tomStates h v m tomControls F % Initial guess if n==20 x0 = {icollocate({v == 0; h == 0 m == m0}) collocate(F == Fm)}; else x0 = {icollocate({v == vopt; h == hopt m == mopt}) collocate(F == Fopt)}; end % Box constraints cbox = {icollocate({0 <= v; 0 <= h mf <= m <= m0 0 <= F <= Fm})}; % Boundary constraints cbnd = {initial({v == 0; h == 0; m == m0}) final({m == mf})}; D = alpha*v.^2.*exp(-beta*h); g = g0; % or g0*r02./(r0+h).^2; % ODEs and path constraints ceq = collocate({dot(h) == v m*dot(v) == F*c-D-g*m dot(m) == -F}); % Objective objective = -1e-4*final(h); %% Solve the problem options = struct; options.name = 'Goddard Rocket'; solution = ezsolve(objective, {cbox, cbnd, ceq}, x0, options); % Optimal v and more to use as starting guess vopt = subs(v, solution); hopt = subs(h, solution); mopt = subs(m, solution); Fopt = subs(F, solution); end t = subs(collocate(t),solution); v = subs(collocate(vopt),solution); h = subs(collocate(hopt),solution); m = subs(collocate(mopt),solution); F = subs(collocate(Fopt),solution);
Problem type appears to be: lpcon
Starting numeric solver
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Goddard Rocket f_k -10.807604031688655000
sum(|constr|) 0.000418640016850601
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) -10.807185391671805000
f(x_0) 0.000000000000000000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 314 ConJacEv 314 Iter 105 MinorIter 1138
CPU time: 0.515625 sec. Elapsed time: 0.516000 sec.
Problem type appears to be: lpcon
Starting numeric solver
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Goddard Rocket f_k -10.822093413609092000
sum(|constr|) 0.006675134485967856
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) -10.815418279123124000
f(x_0) -10.807604031688605000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 32 ConJacEv 32 Iter 25 MinorIter 596
CPU time: 0.234375 sec. Elapsed time: 0.234000 sec.
Problem type appears to be: lpcon
Starting numeric solver
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Goddard Rocket f_k -10.824517135825488000
sum(|constr|) 0.001243055559126850
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) -10.823274080266360000
f(x_0) -10.822093413609082000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 58 ConJacEv 58 Iter 25 MinorIter 1152
CPU time: 0.765625 sec. Elapsed time: 0.765000 sec.
Plot result
subplot(2,1,1) plot(t,v/1e3,'*-',t,h/1e5,'*-',t,m/1e2,'*-'); legend('v','h','m'); title('Goddard Rocket state variables'); subplot(2,1,2) plot(t,F,'+-'); legend('F'); title('Goddard Rocket control');