Jumbo Crane Container Control
Contents
Problem description
Time-optimal control of a Jumbo Container Crane avoiding an obstacle.
Crane dynamics described in the book: Informatics in control automation and robotics II DOI 10.1007/978-1-4020-5626-0 , Springer, 2007, pp.79-84. T.J.J. van den Boom, J.B. Klaassens, R. Meiland Real-time optimal control for a non linear container crane using a neural network
Optimal control problem by: W.L. De Koning, G Fitie and L.G. Van Willigenburg
Programmers: Gerard Van Willigenburg (Wageningen University) Willem De Koning (retired from Delft University of Technology)
% Copyright (c) 2009-2009 by Tomlab Optimization Inc.
Problem setup
% Array with consecutive number of collocation points narr = [10 10 40]; toms t tf % Free final time toms ho1 for i=1:length(narr)
p = tomPhase('p', t, 0, tf, narr(i), [], 'cheb'); setPhase(p) tomStates x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6 tomControls u1 u2 x = [x1; x2; x3; x4; x5; x6]; % Crane parameters gr = 9.81; He = 50; Jh = 35.6; Jt = 13.5; le = 40; ht = 50; mc = 47000; mt = 33000; Nh = 26.14; Nt = 16.15; rh = 0.6; rt = 0.5; xol = 8; xor = 15; hob = 15; % Initial & terminal states xi = [0; 0; 0; 0; 50; 0]; xf = [50; 0; 0; 0; 50; 0]; % Initial guess if i==1; x0 = {tf==20.4; ho1==0; icollocate({x1 == 50*t/20; x2 == xi(2) x3 == xi(3); x4 == xi(4); x5 == xi(5); x6 == xi(6)}) collocate({u1 == -2000; u2 == -5000})}; else x0 = {tf==tfopt; icollocate({x1 == xopt1; x2 == xopt2 x3 == xopt3; x4 == xopt4; x5 == xopt5; x6 == xopt6}) collocate({u1 == uopt1; u2 == uopt2})}; end % Box constraints cbox = {15 <= tf <= 30; -4200 <= collocate(u1) <= 4200 -11490 <= collocate(u2) <= 11490}; % Boundary constraints cbnd = {initial(x == xi), final(x == xf)}; Gt = Jt*Nt*Nt/(rt*rt); Gh = Jh*Nh*Nh/(rh*rh); st = sin(x3); ct = cos(x3); Ft = (Nt/rt)*u1; Fh = (Nh/rh)*u2; d2x = (mc+Gh)*Ft-mc*Fh.*st+mc*gr*Gh*st.*ct+mc*Gh*x5.*x4.*x4.*st; d2x = d2x./((mc+Gh)*(mt+Gt)+mc*Gh*(1-ct.*ct)); % xc is the container x position against time xc = x1+x5*sin(x3); % hc is the height of the container against time hc = ht-x5*cos(x3); % ho is the height of the obstacle at the container x position. %ho = ifThenElse(xc<=xol,0,ifThenElse(xc>=xor,0,hob)); % do is the distance to the obstacle from the container. do = max(max(xol-xc,xc-xor),hc-ho1); % Path constraint - Distance to obstacle should always be >= 0 % and height should always be >= 0. % Test 300 points, evenly spaced in time. pth = {atPoints(linspace(0,tf,300),{do>=0,hc>=0}),ho1>=hob}; % ODEs ode = collocate({ dot(x1) == x2 dot(x2) == d2x dot(x3) == x4 dot(x4) == (-2*x6.*x4-gr*st-d2x.*ct)./x5 dot(x5) == x6 dot(x6) == (Fh+mc*x5.*x4.*x4+mc*gr*ct-mc*d2x.*st)/(mc+Gh) }); % Objective objective = tf;
Solve the problem
options = struct;
if i==1
% To improve convergece, we make the obstacle constraint softer,
% by including it in the ojbective rather than as a hard constraint
% in the first iteration.
% This is necessary because of the very nonlinear properties of this
% constraint.
pth = pth{1};
objective = objective - 2*ho1;
end
options.name = 'Crane with obstacle';
solution = ezsolve(objective, {cbox, cbnd, pth, ode}, x0, options);
tfopt = subs(tf,solution);
xopt1 = subs(x1,solution);
xopt2 = subs(x2,solution);
xopt3 = subs(x3,solution);
xopt4 = subs(x4,solution);
xopt5 = subs(x5,solution);
xopt6 = subs(x6,solution);
uopt1 = subs(u1,solution);
uopt2 = subs(u2,solution);
Problem type appears to be: lpcon
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Crane with obstacle f_k -34.674715981432669000
sum(|constr|) 0.000000101978588531
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) -34.674715879454084000
f(x_0) 20.399999999999999000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 356 ConJacEv 356 Iter 95 MinorIter 8525
CPU time: 6.875000 sec. Elapsed time: 6.891000 sec.
Problem type appears to be: lpcon
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Crane with obstacle f_k 23.843382233623789000
sum(|constr|) 0.000000280437766914
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 23.843382514061556000
f(x_0) 30.000000000000000000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 17 ConJacEv 17 Iter 13 MinorIter 168
CPU time: 0.406250 sec. Elapsed time: 0.406000 sec.
Problem type appears to be: lpcon
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Crane with obstacle f_k 19.558349883431084000
sum(|constr|) 0.012120632528751712
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 19.570470515959837000
f(x_0) 23.843382233623789000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 102 ConJacEv 102 Iter 44 MinorIter 2859
CPU time: 8.187500 sec. Elapsed time: 8.234000 sec.
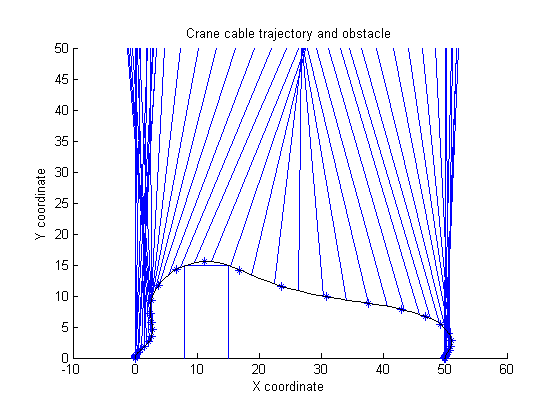
end % Get solution for 50 points, evenly distributed in time. nt = 50; topt = linspace(0,subs(tf,solution),nt); xopt = subs(atPoints(topt,x),solution); % Plot [nt,nx]=size(xopt); clf axis([-10 60 0 50]); axis image; % Draw Obstacle line([xol xol xor xor],[0 hob hob 0]); title('Crane cable trajectory and obstacle'); if nx==6 xtop=xopt(:,1); ytop=50*ones(size(topt)); xbottom=xopt(:,1)+xopt(:,5).*sin(xopt(:,3)); ybottom=50-xopt(:,5).*cos(xopt(:,3)); elseif nx==4 xtop=xopt(:,1); ytop=50*ones(size(topt)); xbottom=xopt(:,1)+40*sin(xopt(:,3)); ybottom=50-40*cos(xopt(:,3)); else error('Crane model should have 4 or 6 state variables'); end % Draw cable trajectory tl=5; lt=length(topt); for k=1:lt line([xtop(k) xbottom(k)],[ytop(k) ybottom(k)]); if tl/lt>0.01; pause(tl/lt); end end hold on ezplot(xc,hc); hold off xlabel('X coordinate'); ylabel('Y coordinate');