Sequential Activation of Metabolic Pathways
a Dynamic Optimization Approach 2009, Diego A. Oyarzuna, Brian P. Ingalls, Richard H. Middleton, Dimitrios Kalamatianosa
Contents
Problem description
The problem is described in the paper referenced above.
% Copyright (c) 2010-2010 by Tomlab Optimization Inc. % Unbranched Pathway (n=4) with MM kinetics kcat0 = 1; kcat1 = 2; kcat2 = 4; kcat3= 3; Km = 1; s0 = 5; V = 0.2; Et = 1; Umax = 1; lam = 0.5; tfmax = 50; % Terminal constraints, compatible with steady state flux V s1f = 0.65; s2f = 0.32; s3f = 0.27; e0f = V*(Km/kcat0/s0 + 1/kcat0); e1f = V*(Km/kcat1/s1f + 1/kcat1); e2f = V*(Km/kcat2/s2f + 1/kcat2); e3f = V*(Km/kcat3/s3f + 1/kcat3);
Problem setup
N = [30 128]; % Number of collocation points toms t tf warning('off', 'tomSym:x0OutOfBounds'); for n = N
p = tomPhase('p', t, 0, tf, n); setPhase(p); tomStates s1 s2 s3 e0 e1 e2 e3 tomControls u0 u1 u2 u3 % Initial guess if n == N(1) x0 = {tf == 2 icollocate({ [s1;s2;s3] == 0 e0 == t/tf e1 == (t-0.2)/tf e2 == (t-1)/tf e3 == (t-1.2)/tf }) collocate({u0 == 1 [u1;u2;u3] == 0})}; else x0 = {tf == tf_init icollocate({ s1 == s1_init; s2 == s2_init; s3 == s3_init e0 == e0_init; e1 == e1_init; e2 == e2_init e3 == e3_init}) collocate({u0 == u0_init u1 == u1_init; u2 == u2_init; u3 == u3_init})}; end % Box constraints cbox = {0.1 <= tf <= tfmax 0 <= icollocate([s1;s2;s3]) <= 100 0 <= icollocate([e0;e1;e2;e3]) <= 1 0 <= collocate([u0;u1;u2;u3]) <= Umax}; % Boundary constraints cbnd = {initial({[s1;s2;s3] == 0; [e0;e1;e2;e3] == 0}) final({s1 == s1f; s2 == s2f; s3 == s3f; e0 == e0f; e1 == e1f; e2 == e2f; e3 == e3f})}; % Michaelis-Mentes ODEs and path constraints ceq = collocate({ dot(s1) == kcat0*s0*e0/(Km + s0) - kcat1*s1*e1/(Km+s1) dot(s2) == kcat1*s1*e1/(Km+s1) - kcat2*s2*e2/(Km+s2) dot(s3) == kcat2*s2*e2/(Km+s2) - kcat3*s3*e3/(Km+s3) dot(e0) == u0 - lam*e0 dot(e1) == u1 - lam*e1 dot(e2) == u2 - lam*e2 dot(e3) == u3 - lam*e3}); % Objective objective = integrate(1 + e0 + e1 + e2 + e3);
Solve the problem
options = struct;
options.name = 'Metabolic Pathways, Unbranched n=4';
solution = ezsolve(objective, {cbox, cbnd, ceq}, x0, options);
% Collect solution as initial guess
s1_init = subs(s1,solution);
s2_init = subs(s2,solution);
s3_init = subs(s3,solution);
e0_init = subs(e0,solution);
e1_init = subs(e1,solution);
e2_init = subs(e2,solution);
e3_init = subs(e3,solution);
tf_init = subs(tf,solution);
u0_init = subs(u0,solution);
u1_init = subs(u1,solution);
u2_init = subs(u2,solution);
u3_init = subs(u3,solution);
Problem type appears to be: qpcon
Starting numeric solver
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2011-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Metabolic Pathways, Unbranched n=4 f_k 6.092698010914444900
sum(|constr|) 0.000001117096574878
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 6.092699128011020100
f(x_0) 4.220507512582272200
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 34 ConJacEv 34 Iter 22 MinorIter 1807
CPU time: 0.703125 sec. Elapsed time: 0.719000 sec.
Problem type appears to be: qpcon
Starting numeric solver
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2011-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Metabolic Pathways, Unbranched n=4 f_k 6.085709091573211700
sum(|constr|) 0.000005873258930019
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 6.085714964832141600
f(x_0) 6.092720075212315400
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 7 ConJacEv 7 Iter 5 MinorIter 2096
CPU time: 8.562500 sec. Elapsed time: 8.610000 sec.
end % Collect data t = subs(collocate(t),solution); s1 = subs(collocate(s1),solution); s2 = subs(collocate(s2),solution); s3 = subs(collocate(s3),solution); e0 = subs(collocate(e0),solution); e1 = subs(collocate(e1),solution); e2 = subs(collocate(e2),solution); e3 = subs(collocate(e3),solution); u0 = subs(collocate(u0),solution); u1 = subs(collocate(u1),solution); u2 = subs(collocate(u2),solution); u3 = subs(collocate(u3),solution);
Plot result
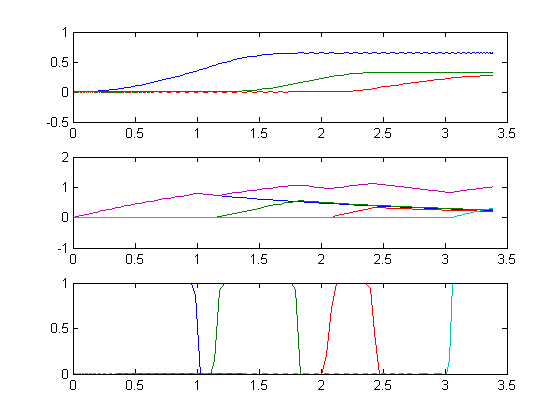
s = [s1 s2 s3]; e = [e0 e1 e2 e3]; r = [u0 u1 u2 u3]; subplot(3,1,1); plot(t,[s1 s2 s3]); subplot(3,1,2); plot(t,[e0 e1 e2 e3 e0+e1+e2+e3]); subplot(3,1,3); plot(t,[u0 u1 u2 u3]);