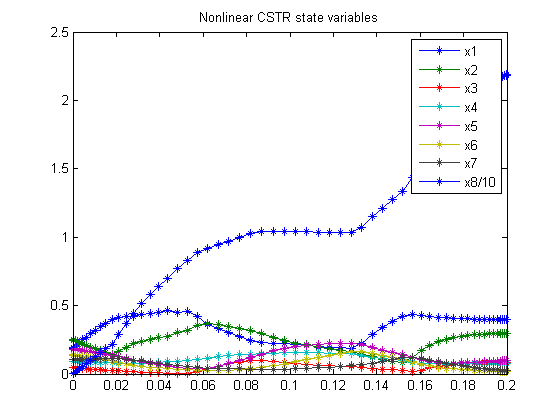
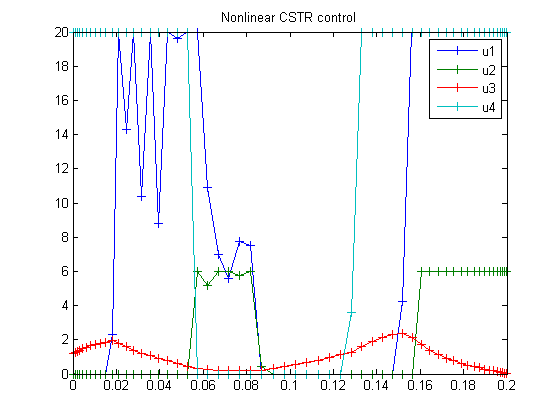
Nonlinear CSTR
Dynamic optimization of chemical and biochemical processes using restricted second-order information 2001, Eva Balsa-Canto, Julio R. Banga, Antonio A. Alonso Vassilios S. Vassiliadis
Case Study III: Nonlinear CSTR
Contents
Problem description
The problem was first introduced by Jensen (1964) and consists of determining the four optimal controls of a chemical reactor in order to obtain maximum economic benefit. The system dynamics describe four simultaneous chemical reactions taking place in an isothermal continuous stirred tank reactor. The controls are the flow rates of three feed streams and an electrical energy input used to promote a photochemical reaction. Luus (1990) and Bojkov, Hansel, and Luus (1993) considered two sub-cases using three and four control variables respectively.
The problem is formulated as follows:Find u1(t), u2(t), u3(t) and u4(t) over t in [t0,tf] to maximize:
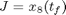
Subject to:
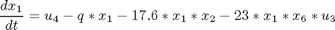
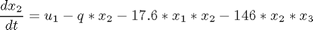
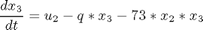
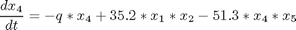
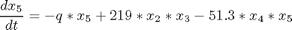
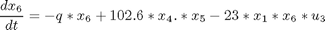
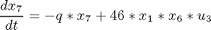
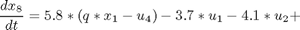
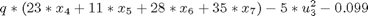
where:
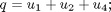
with the initial conditions:
![$$ x(t_0) = [0.1883 \ 0.2507 \ 0.0467 \ 0.0899 \ 0.1804 \ 0.1394 \ 0.1046 \ 0.000]' $$](xnonlinearCSTR_eq38066.png)
And the following bounds on the control variables:
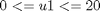
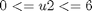
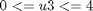
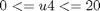
The final time is considered fixed as tf = 0.2.
% Copyright (c) 2007-2008 by Tomlab Optimization Inc.
Problem setup
toms t
Solve the problem, using a successively larger number collocation points
for n=[5 20 60]
p = tomPhase('p', t, 0, 0.2, n); setPhase(p); tomStates x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6 x7 x8 tomControls u1 u2 u3 u4 % Interpolate an initial guess for the n collocation points if n == 5 x0 = {}; else x0 = {icollocate({x1 == x1opt; x2 == x2opt x3 == x3opt; x4 == x4opt; x5 == x5opt x6 == x6opt; x7 == x7opt; x8 == x8opt}) collocate({u1 == u1opt; u2 == u2opt u3 == u3opt; u4 == u4opt})}; end % Box constraints cbox = {icollocate({ 0 <= x1; 0 <= x2; 0 <= x3 0 <= x4; 0 <= x5; 0 <= x6 0 <= x7; 0 <= x8}) collocate({ 0 <= u1 <= 20; 0 <= u2 <= 6 0 <= u3 <= 4; 0 <= u4 <= 20})}; % Boundary constraints cbnd = initial({x1 == 0.1883; x2 == 0.2507 x3 == 0.0467; x4 == 0.0899; x5 == 0.1804 x6 == 0.1394; x7 == 0.1064; x8 == 0}); % ODEs and path constraints % 4.1*u2+(u1+u2.*u4) in another paper, -0.09 instead of -0.099 q = u1+u2+u4; ceq = collocate({ dot(x1) == (u4-q.*x1-17.6*x1.*x2-23*x1.*x6.*u3) dot(x2) == (u1-q.*x2-17.6*x1.*x2-146*x2.*x3) dot(x3) == (u2-q.*x3-73*x2.*x3) dot(x4) == (-q.*x4+35.2*x1.*x2-51.3*x4.*x5) dot(x5) == (-q.*x5+219*x2.*x3-51.3*x4.*x5) dot(x6) == (-q.*x6+102.6*x4.*x5-23*x1.*x6.*u3) dot(x7) == (-q.*x7+46*x1.*x6.*u3) dot(x8) == (5.8*(q.*x1-u4)-3.7*u1-4.1*u2+q.*... (23*x4+11*x5+28*x6+35*x7)-5*u3.^2-0.099)}); % Objective objective = -final(x8);
Solve the problem
options = struct;
options.name = 'Nonlinear CSTR';
solution = ezsolve(objective, {cbox, cbnd, ceq}, x0, options);
% Optimal x and u as starting point
x1opt = subs(x1, solution);
x2opt = subs(x2, solution);
x3opt = subs(x3, solution);
x4opt = subs(x4, solution);
x5opt = subs(x5, solution);
x6opt = subs(x6, solution);
x7opt = subs(x7, solution);
x8opt = subs(x8, solution);
u1opt = subs(u1, solution);
u2opt = subs(u2, solution);
u3opt = subs(u3, solution);
u4opt = subs(u4, solution);
Problem type appears to be: lpcon
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Nonlinear CSTR f_k -21.841502289865446000
sum(|constr|) 0.000000000210556508
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) -21.841502289654890000
f(x_0) 0.000000000000000000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 53 ConJacEv 53 Iter 41 MinorIter 340
CPU time: 0.296875 sec. Elapsed time: 0.297000 sec.
Problem type appears to be: lpcon
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Nonlinear CSTR f_k -21.896802275281694000
sum(|constr|) 0.000000001588543450
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) -21.896802273693151000
f(x_0) -21.841502289865446000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 96 ConJacEv 96 Iter 91 MinorIter 374
CPU time: 1.296875 sec. Elapsed time: 1.297000 sec.
Problem type appears to be: lpcon
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Nonlinear CSTR f_k -21.887245712615979000
sum(|constr|) 0.000000000754547213
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) -21.887245711861432000
f(x_0) -21.896802275281715000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 283 ConJacEv 283 Iter 270 MinorIter 1018
CPU time: 39.375000 sec. Elapsed time: 39.844000 sec.
end
t = subs(collocate(t),solution);
x1 = collocate(x1opt);
x2 = collocate(x2opt);
x3 = collocate(x3opt);
x4 = collocate(x4opt);
x5 = collocate(x5opt);
x6 = collocate(x6opt);
x7 = collocate(x7opt);
x8 = collocate(x8opt);
u1 = collocate(u1opt);
u2 = collocate(u2opt);
u3 = collocate(u3opt);
u4 = collocate(u4opt);
Plot result
figure(1) plot(t,x1,'*-',t,x2,'*-',t,x3,'*-',t,x4,'*-' ... ,t,x5,'*-',t,x6,'*-',t,x7,'*-',t,x8/10,'*-'); legend('x1','x2','x3','x4','x5','x6','x7','x8/10'); title('Nonlinear CSTR state variables'); figure(2) plot(t,u1,'+-',t,u2,'+-',t,u3,'+-',t,u4,'+-'); legend('u1','u2','u3','u4'); title('Nonlinear CSTR control');