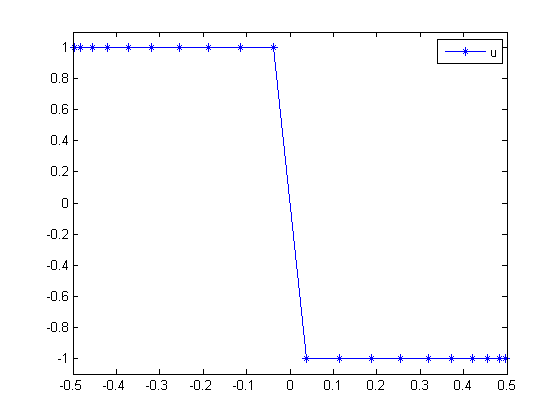
Simple Bang Bang Problem
Function Space Complementarity Methods for Optimal Control Problems, Dissertation, Martin Weiser
Contents
Problem Description
Find u over t in [-0.5; 0.5 ] to minimize:
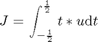
subject to:
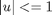
% Copyright (c) 2007-2008 by Tomlab Optimization Inc.
Problem setup
toms t p = tomPhase('p', t, -0.5, 1, 20); setPhase(p); tomStates x tomControls u % Initial guess x0 = {collocate(u == 1-2*(t+0.5)) icollocate(x == 1-2*(t+0.5))}; % Box constraints cbox = {-1 <= icollocate(x) <= 1 -1 <= collocate(u) <= 1}; % ODEs and path constraints ceq = collocate(dot(x) == 0); % Objective objective = integrate(t.*u);
Solve the problem
options = struct;
options.name = 'Simple Bang Bang Problem';
solution = ezsolve(objective, {cbox, ceq}, x0, options);
t = subs(collocate(t),solution);
u = subs(collocate(u),solution);
Problem type appears to be: lp
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Simple Bang Bang Problem f_k -0.250490325030179710
sum(|constr|) 0.000000000000810402
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) -0.250490325029369300
f(x_0) 0.000000000000000000
Solver: CPLEX. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
CPLEX Dual Simplex LP solver
Optimal solution found
Plot result
figure(1); plot(t,u,'*-'); legend('u'); ylim([-1.1,1.1]);