Zermelos problem (version 1)
Contents
Problem description
Time-optimal aircraft heading through air in motion
Applied Optimal Control, Bryson & Ho, 1975. Problem 1 on page 77.
Programmers: Gerard Van Willigenburg (Wageningen University) Willem De Koning (retired from Delft University of Technology)
% Copyright (c) 2009-2009 by Tomlab Optimization Inc.
Problem setup
% Array with consecutive number of collocation points narr = [20 40]; toms t tf % Free final time for n=narr
p = tomPhase('p', t, 0, tf, n); setPhase(p) tomStates x1 x2 tomControls u1 % Initial & terminal states xi = [-2; 0]; xf = [0.5; -1.6]; % Initial guess if n==narr(1) x0 = {tf == 2; icollocate({x1 == xi(1); x2 == xi(2)}) collocate({u1 == pi})}; else x0 = {tf == tfopt; icollocate({x1 == xopt1; x2 == xopt2}) collocate({u1 == uopt1})}; end % Box constraints cbox = {1 <= tf <= 10}; % Boundary constraints cbnd = {initial({x1 == xi(1); x2 == xi(2)}); final({x1 == xf(1); x2 == xf(2)})}; % ODEs and path constraints wh = exp(-x1.*x1-x2.*x2+0.25); v=1; dx1 = v*cos(u1)+x2.*wh; % x2*wh: motion of air in x1 direction dx2 = v*sin(u1)-x1.*wh; % -x1*wh: motion of air in x2 direction ceq = collocate({ dot(x1) == dx1 dot(x2) == dx2}); % Objective objective = tf;
Solve the problem
options = struct;
options.name = 'Zermelo Flight Trajectory';
solution = ezsolve(objective, {cbox, cbnd, ceq}, x0, options);
tfopt = subs(tf,solution);
xopt1 = subs(x1,solution);
xopt2 = subs(x2,solution);
uopt1 = subs(u1,solution);
Problem type appears to be: lpcon
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Zermelo Flight Trajectory f_k 3.682008477941141100
sum(|constr|) 0.000000007014146326
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 3.682008484955287200
f(x_0) 2.000000000000000000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 147 ConJacEv 147 Iter 133 MinorIter 176
CPU time: 0.328125 sec. Elapsed time: 0.329000 sec.
Problem type appears to be: lpcon
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2010-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Zermelo Flight Trajectory f_k 3.682008478157506200
sum(|constr|) 0.000000039753880299
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 3.682008517911386400
f(x_0) 3.682008477941141100
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 37 ConJacEv 37 Iter 24 MinorIter 109
CPU time: 0.171875 sec. Elapsed time: 0.172000 sec.
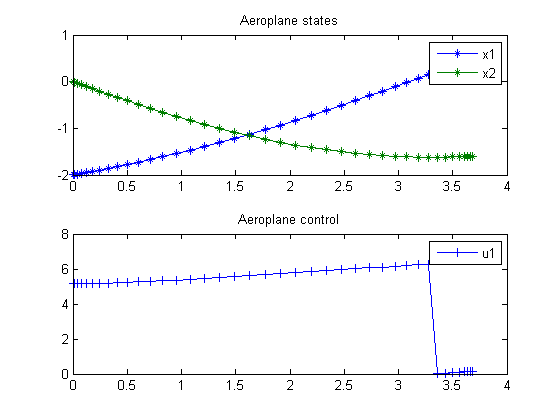
end % Get solution t = subs(collocate(t),solution); x1 = subs(collocate(x1),solution); x2 = subs(collocate(x2),solution); u1 = subs(collocate(u1),solution); %Bound u1 to [0,2pi] u1 = rem(u1,2*pi); u1 = (u1<0)*2*pi+u1; % Plot final solution figure(1); subplot(2,1,1) plot(t,x1,'*-',t,x2,'*-'); legend('x1','x2'); title('Aeroplane states'); subplot(2,1,2) plot(t,u1,'+-'); legend('u1'); title('Aeroplane control');